http://learn-mobiletechnology.blogspot.ae/
Saturday, October 26, 2013
HARDWARE RESET A NOKIA LUMIA 920
Hardware reset
If the phone hardware is jammed,
not reset the Windows Live ID or remove any of your data. Because
the user cannot remove the battery to reset the phone the
phone has a special electronic circuit which cuts the phone power
when the volume down and power keys are pressed for 5 seconds.
To perform the hardware reset press the Volume down and Power
keys and hold them for 5 seconds. The phone screen will turn black
(phone is off). Then press the Power key to turn on the phone.
Software / operating system (OS) reset
The software / operating system (OS) reset returns the phone to its out-of-the-box state. Note that this
procedure erases all consumer data! Always first try to perform a hardware reset.
Option 1: About menu
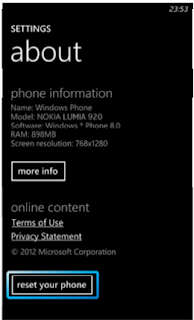
- Use this option if the consumer knows the lock code
- This option warns the consumer about data loss!
- Tap Settings > About > reset your phone
Option 2: Hardware key combination
- Use this option if the phone is locked and the consumer does not know the code
- Note: no warning about data loss!
Follow next steps to perform OS reset with phone keys.
Step 1
Make sure the phone is turned Off.
Press and hold the Volume down
exclamation mark is shown on the screen
Step 2
Input the following key combination:
1. Volume up
2. Volume down
3. Power
4. Volume down
Step 3
The phone will reset and boot up
automatically
©samsung gt-i8350 hard reset

SAMSUNG GT- i8350
keep pushed vol. down + camera + home and switch
on,
will see "format" on display then press HOME button
you will be asked for confirmation ,press HOME button again
your handset will be formatted in seconds
be care full, format clean security code and ,offcourse, erase all user data.
after format the phone reinstall automatic all apps originals.
Thursday, October 3, 2013
MOBILE TERMINOLOGIES
Symbian
Definition: software licensing company established in June 1998 by Psion,
Nokia, Ericsson, and Motorola with the aim of developing and standardising
software technology for mobile computing devices and mobile phones
Note: Symbian is owned by Ericsson, Nokia, Matsushita (Panasonic), Motorola, Psion, Siemens, and Sony Ericsson. Symbian enables common characteristics among portable phones of different manufacturers with regard to wireless information, network, content, messaging, and other functions, in effect aiming at a de facto standard. Symbian has created the Symbian operating system.
General definition for common use: A software licensing company, owned by wireless industry leaders, which is the supplier of an advanced, open, standard operating system for data-enabled wireless devices.
Java ; Java language
Definition: object-oriented programming language developed by Sun Microsystems,
which is intended to be hardware and software independent
Note: Java can be used, for example, to program web services. Java has an extensive library of routines for TCP/IP protocols like HTTP and FTP. Java applications can access objects across the Internet via URL addresses as easily as on the local file system.
General definition for common use: A programming language developed by Sun Microsystems. Some Nokia phones support the downloading of Java(tm) applications.
SyncML
Definition: open industry standard for universal synchronisation of remote data
and personal information across multiple networks, platforms, and devices
General definition for common use: An open standard that enables synchronisation of data between compatible devices, applications, and networks, which means that a consistent set of data is always available on any device or application. SyncML is based on Extensible Markup Language (XML).
series 60 user interface ; series 60 UI
General definition for common use: A one-hand operated user interface for imaging phones. The Nokia series 60 user interface has a large colour display of 176 x 206 pixels.
Bluetooth
Definition: technology designed to be embedded in electronic devices in order
to provide wireless and seamless connections over short distances, thus
providing an alternative to cable-based interfaces currently in use to link
computers and computer peripherals
General definition for common use: A technology that provides short-range radio links to allow mobile computers, mobile phones, digital cameras, and other portable devices to communicate with each other without cables. A Nokia mobile device with Bluetooth support allows the user to connect wirelessly to another compatible Bluetooth device within a short range.
Open Mobile Alliance ; OMA
Not: Open Mobile Architecture
Definition: organisation that acts as a mobile industry standards forum aiming
at interoperable mobile services across geographic areas, network operators,
and mobile terminals and at an open standards-based framework that permits
services in a multi-vendor environment
Note: The initiative for OMA was launched by Nokia and more than nineteen other industry leaders to define an open architecture to enhance mobile services. The principles of the Open Mobile Alliance are that products and services are based on open, global standards, protocols, and interfaces; the application layer is bearer-independent; the architecture framework and service enablers are independent of the operating system (OS); and applications and platforms are interoperable, providing geographic and inter-generational roaming. The Open Mobile Alliance was created by joining the Open Mobile Architecture initiative and WAP Forum. In addition, the Location Interoperability Forum (LIF), SyncML, MMS Interoperability Group (MMS-IOP), and
General definition for common use: An organisation that is designed to be the centre of mobile application standardisation work, helping the creation of interoperable services that will meet the needs of the user across countries, operators, and mobile terminals. The Open Mobile Alliance was formed in June 2002 by nearly 200 companies representing the world's leading mobile operators, device and network suppliers, information technology companies, and content providers.
XHTML ; extensible
hypertext markup language
Definition: hypertext markup language (HTML) to which new elements and
attributes can be defined and added and that is an application of extensible
markup language (XML)
Note: In XHTML, all HTML markup elements and attributes (the language of HTML) are supported. Unlike HTML, however, XHTML can be extended by anyone that uses it. New elements and attributes can be defined and added to those that already exist, creating new ways to embed content and programming on a web page.
General definition for common use: A markup language that consists of HTML elements combined with the syntax of XML. The specification for XHTML is a web standard.
wireless markup language ;
WML
Definition: markup language that is designed for the representation of data via
wireless access
Note: WML is part of the wireless application protocol (WAP). WML is similar to
HTML but more restricted.
General definition for common use: A language describing the structure of data
that allows the data of web pages to be presented on mobile devices via
wireless access.
wireless application
protocol ; WAP
Definition: open, global standard for total mobile solutions, including
communication between a mobile handset and the Internet or other computer
applications
Note: WAP-based technology enables the design of advanced, interactive, and real-time mobile services, such as mobile banking or Internet-based news services, which can be used on mobile devices. The WAP specification enables solutions from various suppliers to work consistently for end-users on digital networks. Feature/application: Internet.
Context: 1. An error has occurred in the WAP gateway; The WAP application can be used to access Internet services which are based on the Wireless Access Protocol (WAP).
General definition for common use: An open international standard for applications that use wireless communication. The main application based on WAP is Internet access from a mobile device, which can be used, for example, for banking, e-mail exchange, ticket purchase, and news services.
multimedia messaging service
; multimedia message service ; MMS
Definition: messaging service for sending and receiving multimedia messages
Note: The multimedia messaging service combines conventional text messages with
richer content types, such as photographs, images, voice clips, and video
clips. The multimedia messaging service is used with multimedia terminals, for
example WAP clients, which can receive and process multimedia messages.
General definition for common use: A messaging service that combines conventional text messages with other content types, such as photographs, images, sound clips, and video clips. The multimedia messaging service is used with multimedia phones, which can receive and process multimedia messages.
general packet radio service ;
GPRS
Definition: mobile service which gives packet-switched access over GSM to
external data networks
Note: The main objective of GPRS is to offer access to standard data networks
such as TCP/IP, X.25, and connectionless network protocol (CLNP).
Feature/application: WAP.
General definition for common use: A GSM data transmission technique that transmits and receives data in packets. GPRS offers a permanent connection between the wireless device and the network.
global positioning system ;
GPS
Definition: satellite-based positioning system that is used for reading
geographical position and as a source of the accurate co-ordinated universal
time
push to talk
Not: PTT ; push-to-talk
Definition: one-way communication function in a mobile phone which enables a user to talk to another user or a selected user group, while the recipient(s) is only listening
Note: Push to talk is activated by pressing the push to talk key or equivalent in the phone. In a user group, the turns to speak are requested by pressing the push to talk key and granted on a first-come-first-served basis. Because of Intellectual Property Rights, the hyphenated form push-to-talk is not recommended at Nokia.
General definition for common use: A one-way communication function in a mobile phone which lets one user at a time talk to another user or a selected user group. Push to talk is activated by pressing the push to talk key or equivalent on the phone. In a user group, the turns to speak are requested by pressing the push to talk key and granted on a first come, first served basis.
POP3 ; Post Office Protocol,
version 3
Definition: version of the post office protocol (POP) which permits a
workstation to dynamically access a maildrop on a server
Note: POP3 is not intended to provide extensive manipulation operations of mail on the server; normally, mail is downloaded and then deleted. POP3 is defined in RFC 1939.
General definition for common use: A version of the post office protocol that is used to store and retrieve e-mail or Internet mail messages. POP3 is used in conjunction with the simple mail transfer protocol (SMTP).
IMAP ; Internet message access
protocol
Definition: message access protocol that is used for accessing the remote
mailbox
Note: Feature/application: Messaging.
simple mail transfer
protocol ; SMTP
Definition: Internet protocol which provides e-mail services
Note: The SMTP standard is used extensively on the Internet for transferring
e-mail messages between computers. It defines exactly how the message will be
sent, what message format it has, and so on. Feature/application: Error notes.
Context: 1. SMTP server refused the connection.
General definition for common use: A protocol that is used to transfer e-mail messages. Usually SMTP is used only for sending.
wireless
LAN ; wireless local area network ; WLAN
Not: cordless LAN
Definition: local area network using wireless connections as transmission path
Note: In a wireless LAN, radio, microwave, or infrared links take the place of
physical cables. Note that the abbreviation WLAN can in some contexts be
confusing, because it can also mean wired LAN.
Saturday, August 24, 2013
Nokia BB5 Cell Phone Basic Technology
BASE BAND 5
Baseband 5, generation 5.0 (BB5) technology is the beginning of the development of 3G, NOKIA BB5 Cell Phone until now been developed into 4G technology. Data access speed is very fast, so it can have features that are very powerful, such as internet access speed up to 384 kbps, Video Streaming, Broadcast TV (DVB-H), etc..
Increasingly powerful computerized system, which is used Microprocessor almost equivalent to a desktop computer or laptop, so the technology NOKIA BB5 Cell Phone not only referred to as mobile phones, but computers and mobile media. Features that are owned including: LCD TFT 18 Mega Colors, resolution up to 5 Mega pixel camera, Wi-Fi / Wireless, LAN, GPS, Navigation, etc.
Increasingly powerful computerized system, which is used Microprocessor almost equivalent to a desktop computer or laptop, so the technology NOKIA BB5 Cell Phone not only referred to as mobile phones, but computers and mobile media. Features that are owned including: LCD TFT 18 Mega Colors, resolution up to 5 Mega pixel camera, Wi-Fi / Wireless, LAN, GPS, Navigation, etc.
NOKIA BB5 Cell Phone technology has several categories, adjusted for purchasing power of consumers, the specifications have certainly not all the same. NOKIA BB5 Cell Phone including specification differences lies in Microprocessor used, as will be explained below.
NOKIA BB5 CELL PHONE(RAPGSMv1)
Nokia cell phone that use the processor RAPGSMv1 including ; 3250, 5200, 5300, 5500, 6085, 6125, 6270, 6300, 7370, E50, E62. The processor RAPGSMv1 is the development of processor Tiku (Nokia DCT4 + processor for example 7200, 7600, 6230, etc.) differences among Tiku and RAPGSMv1 IMEI is located on storage security that has been integrated within RAPGSMv1. RAPGSMv1 protocol not supports WCDMA or 3G, only GSM EDGE Class 10 GPRS which can be facilitated.
Specifications RAPGSMv1
- MCU Subsystem, ARM926 main Processor
- MCU Peripheral e.g. CBUS IF, USB IF, and SIM IF
- DSP Subsystem, Lead3 PH3
- DSP Peripheral e.g. speech codec
- PDRAM 4Mbit
- IMEI Security Storage
- Phone Specific Subsystem
- GSM Coder
- Interface for User Interface
- ASIC Clock and reset control
- Clock Slicer, It is a block that get low amplitude differential sinusoidal clock wave (RfClkP & RfClkN 38.4mHz)
- In and give an accurate square wave out (SYSCLK 19.2mHz)
- RF Codec that include ADC and DAC converters for the RF signal
RAPGSMv1 given supply voltage Vcore = 1.4 Volt by TAHVO, while RETU will provide voltage VIO = 1.8 Volt and VRFC = 1.8 Volt. RF Clock = 38.4 MHz supplied from the RF module, while Sleep Clock = 32.768 kHz RETU generated from the External Oscillator.
MEMORY
Nokia BB5 cell phone using RAPGSMv1 only need one Combo Memory, Combo Memory neither is a combination of NOR Flash and SDRAM.
NOR Flash (Flash CMT) is used to store program code MCU and DSP, also stores; Tuning Values, Certificates ID, Security IMEI. NOR Flash type has the data capacity of 256Mb.
SDRAM (CMT SDRAM) is used as temporary data storage (Dynamic Data Storage), which has a data capacity of 128 MB.
SDRAM (CMT SDRAM) is used as temporary data storage (Dynamic Data Storage), which has a data capacity of 128 MB.
RF MODULE PART
RF module on the Nokia cell phone type has several important parts, including:
RF module on the Nokia cell phone type has several important parts, including:
- RF processor using AHNE 401A
- GSM Front End Module, is a combination antenna switch and PA
- External VCO (Voltage Control Oscillator)
- VCTCXO
- SAW Filters
NOKIA BB5 Cell Phone (RAP3Gv2)
Nokia BB5 cell phones using RAP3Gv2 include; 6630, 6680, 6681, E60, E70, N70, N71, N72, N90, N91. RAP3Gv2 supports WCDMA Cellular Protocol or commonly referred to 3G. Different with Nokia BB5 cell phones using RAPGSMv1, RAP3Gv2 require additional processor, and then on the phone this type always uses 2 processors inside. Additional processor that is HELEN/OMAP (Open Multimedia Audio Processor), this processor that will assist in managing the UI (User Interface) and multimedia mobile phones such as; Camera, MMC, LCD, Keypad, etc.. OMAP functions can be likened to a Subsystem Body on the UPP Nokia WD2, whereas RAP3G Subsystem is part of the brain in UPP Nokia DCT4.
Schema Baseband BB5 (RAP3Gv2)
RAP3Gv2 (Radio Application Processor)
RAP3Gv2 has a RAM memory that has integrated in it which is used to store software: MCU Subsystem, DSP Subsystem, the Certificate ID and Security IMEI.
In general, RAP3Gv2 function as:
- Processor Subsystem (PSS), is the main processing all phone functions
- MCU Peripheral, this subsystem functions such as: MCU Core, Core Boot, Thumb Memory Interface, etc.
- DSP Peripheral, this Subsystem functions such as: DSP Core with the DMA Controller and State Generator, DSP Cache RAM, Storing and Variable Manipulation Software, etc.
RAP3Gv2 get Vcore voltage = 1.4 Volt TAHVO generated, and voltage VIO = 1.8 volts provided by RETU.
HELEN/OMAP (Open Multimedia Audio Processor)
HELEN/OMAP only on the Nokia BB5 using RAP3Gv2, which RAP3Gv2 requires HELEN/OMAP who will process the application operating system (EPOC) and set the UI (User Interface) and Multimedia phone. OMAP has several functions, including :
- Camera interface
- Display interface
- Bluetooth interface
- SD interface
- USB interface
- Keyboard interface
Block Diagram of OMAP could be shown like the picture below :
Memory
Memory as data storage required by Nokia BB5 RAP3G v2 three memory that will be accessed by RAP3G and OMAP. Memory is as below :
- APE Combo Memory accessed by the OMAP processor. This memory contains the application data and Data User Interface settings. APE Combo Memory consists of NAND Flash and DDRAM are integrated in one IC. NAND Flash can store data at 256 MB while DDRAM has a capacity of 256MB data.
- NOR Flash (CMT Memory) is memory that contains vital data containing the main function of the phone firmware, calibration and certificate ID, IMEI and Security. This memory will be accessed by RAP3G. Capacity data storage in NOR Flash 64 MB.
- SDRAM (CMT SDRAM) is used as temporary data storage (Dynamic data storage), which has a capacity of 64MB of data.
RF Module Part
Nokia BB5 Cell Phone using RAP3Gv2 has two frequency modes, GSM and WCDMA. WCDMA transceiver has a faster data speeds. RF module architecture of this type will very complicated, parts of which this RF module includes:
- HINKU, is RF Processor for receiver
- VINKU, is RF Processor for transmitting
- Switch Antenna / Duplexer
- WCDMA Power Amplifier
- DC/DC Converter for WCDMA PA
- GSM Power Amplifier
- VCO (voltage control oscillator)
- VCTCXO for System Clock
Nokia BB5 Cell Phone (RAP3G v3)
Nokia BB5 Cell Phone phones using RAP3Gv3 include 6151, 6233, 6280. RAP3Gv3 already support WCDMA Cellular Protocol or commonly called 3G. This processor latest generation of RAPGSMv1, deference with RAP3Gv2 as requiring OMAP for additional processor, RAP3Gv3 not need OMAP. So Nokia BB5 Cell Phone using RAP3Gv3 there is only one main course Processor.
Schematic Diagram of Baseband Nokia BB5 Cell Phone (RAP3Gv3)
Specifications RAP3Gv3
- MCU Subsystem, ARM256 main Processor
- DSP Subsystem, Lead3 PH3
- DSP peripherals
- PDRAM 4Mbit
- IMEI Security storage
- Phone Specific Subsystem
- GSM Coder
- Interfaces for user interface, SIM, MMC, LCD, Keyboard
- Accessories Interface
- Handling of Baseband – RF Interface
RAPGSMv3 given supply voltage VCORE = 1.4 Volt produce by TAHVO, while Retu will provide voltage VIO = 1.8Volt and VRFC = 1.8Volt. RF Clock = 38.4MHz supplied from the RF module, while Sleep clock = 32.768kHz generated Retu from external oscillator
Memory
As data storage required by Nokia BB5 Cell Phone RAP3Gv3 used two CMT Memory:
- NOR Flash (CMT Flash) with a capacity of 256 MB of data storage, used to store program code MCU and DSP, also stores Tuning Values, ID Certificates, Security IMEI
- SDRAM (CMT SDRAM) is used as a temporary data storage (Dynamic data storage), which has a data capacity of 128 MB
RF Module Part
Nokia BB5 Cell Phone using RAP3Gv3 has two frequency modes, GSM and WCDMA. WCDMA use 3G facilities that have a faster speed data transceiver. Parts including RF module:
- RF Processor using PIHI
- GSM Front End Module, is a combination antenna switch and
- Power Amplifier
- WCDMA Power Amplifier
- DC/DC Converter for WCDMA PA
- External VCO (voltage control oscillator) for RX/TX GSM and
- RX/TX WCDMA
- VCTCXO for System Clock
- SAW Filter
PIHI
have several functions, including
have several functions, including
- SAW Filter for RX
- LNA
- GSM Balun
- BB Gain Amplifier
- DC Compensation for RX
- Internal PLL and Oscillator for WCDMA RX
- PLL for external Oscillator
- Current to Voltage Converter (in TX)
- TX Mixer
- TX Preamplifier
- TX SAW Filter for GSM 1800/1900
- TX Power Control Reference Voltage & Current Source
Nokia BB5 Cell Phone (RAP3GSv2.0E)
Schematic Diagram of Baseband Nokia BB5 Cell Phone (RAP3GSv2.0E)
Processor Nokia BB5 Cell Phone using RAP3GSv2E has the same specs with RAP3Gv2 is using ARM926 and Lead3 PH3 DSP is integrated in RAP3G. The difference, RAP3GSv2.0E already have combo Memory so no need to use the Combo External Flash. Memory Combo has been stored in structured RAP3G and made one IC.
RAP3GSv2E given by IC AVILMA VCORE voltage of 1.35 V, while the VIO voltage supplied by the IC BETTY of 1.8 V.
Combo Memory will be accessed by RAP3G for data processing, Combo memory of them is :
- NOR Flash (CMT Memory) is memory that contains data vital primary function of the phone. Contains the firmware, calibration, certificate ID, IMEI and Security. NOR Flash memory has a capacity of 128MB.
- SDRAM (CMT SDRAM) is used as data storage temporary (Dynamic data storage), DDR SDRAM has 128MB capacity.
In Nokia BB5 Cell Phone for type E61, E61i, N73, N80, N92 using two Processor, RAP3GS and Helen / OMAP (Open Multimedia Audio Processor). OMAP version used is the ARM1710, while for the Nokia N93 using the OMAP ARM2420 version. This processor that will process the application operating system (EPOC) and set the UI (User Interface) and Multimedia Mobile Phone. OMAP has several functions, including :
- Camera interface
- Display interface
- Bluetooth interface
- SD interface
- USB interface
- Keyboard interface
- SSI for communication with RAP3GS
- GPS
- TCS Modem Chipset
- Imaging Video Accelerator
- 2D-3D Graphic Accelerator
Schematic Diagram of OMAP 1710
Schematic Diagram of OMAP 2420
Memory
Memory for storage of data required by OMAP is APE Combo Memory. This memory contains data applications and data settings User Interface. APE Combo Memory itself consists of NAND Flash and DDRAM are integrated in one IC. NAND Flash can store 1GB of data while DDRAM has a data capacity of 512MB
RF Module Part
Nokia BB5 Cell Phone using RAP3Gv2 has two frequency modes, GSM and WCDMA. WCDMA use 3G facilities that have a faster speed data transceiver. Parts of the RF module of which this :
RF Processor using PIHI
- GSM Front End Module, is a combination antenna switch and
- Power Amplifier
- WCDMA Power Amplifier
- DC / DC Converter for WCDMA PA
- External VCO (voltage control oscillator) for RX/TX GSM and RX/TX WCDMA
- VCTCXO for System Clock
- SAW Filter
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)





